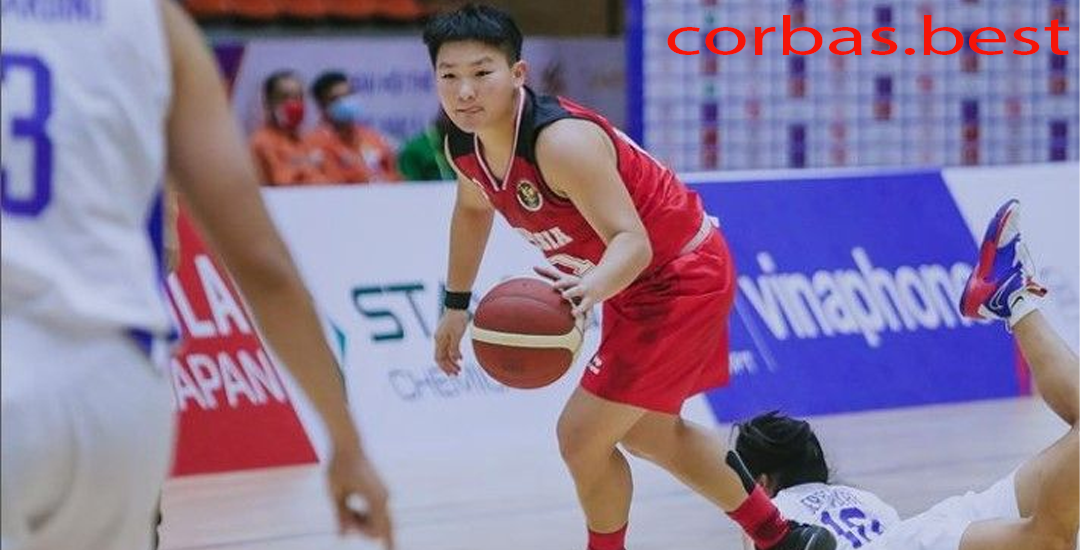
Nathania Claresta Orville: Atlet Basket Putri Asli Jambi yang Berjaya Membawa Medali Emas
Pendahuluan Nathania Claresta Orville Indonesia dikenal sebagai negara yang kaya akan keberagaman budaya dan sumber…
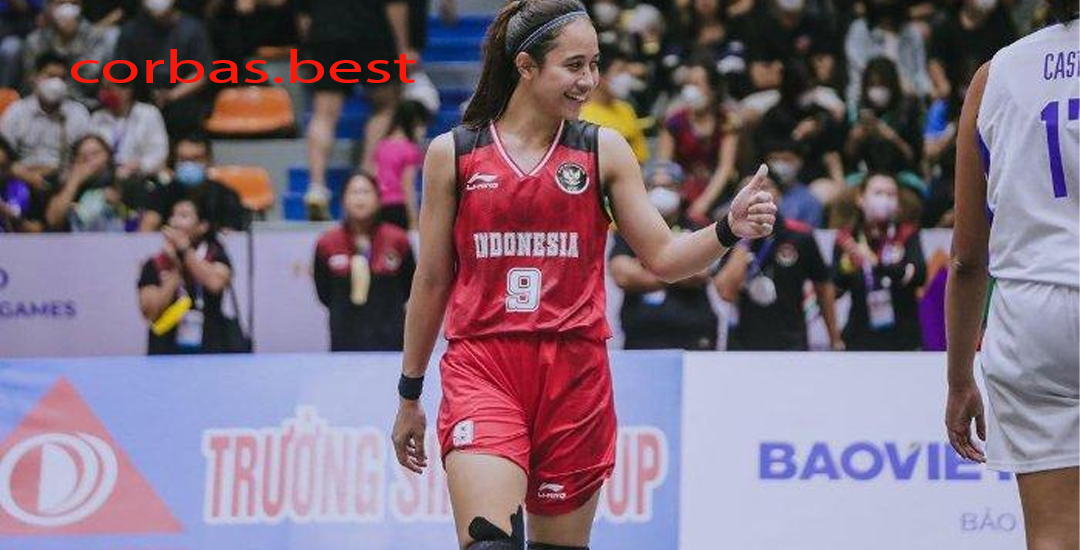
Ayu Sriartha: Pilar Utama Timnas Basket Indonesia di SEA Games
Pendahuluan Ayu Sriartha Basket adalah salah satu cabang olahraga yang cukup populer di Indonesia dan…
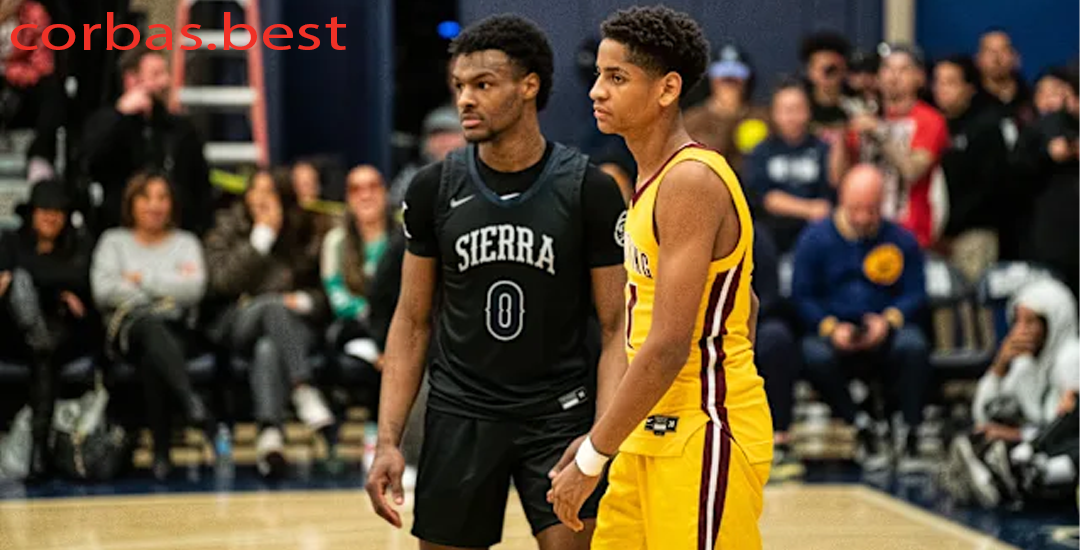
Kiyan Anthony dan Bronny James: Mengikuti Jejak Ayah Mereka dalam Dunia Basket
Pendahuluan Kiyan Anthony dan Bronny James Dalam dunia olahraga, kisah keluarga yang menonjol sering kali…
RJ Barrett: Pemain Serba Bisa yang Dipilih New York Knicks dan Pernah Satu Tim dengan Zion
Pendahuluan RJ Barrett merupakan salah satu bintang muda potensial di dunia bola basket NBA. Pemain…
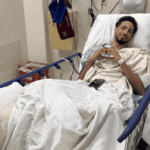
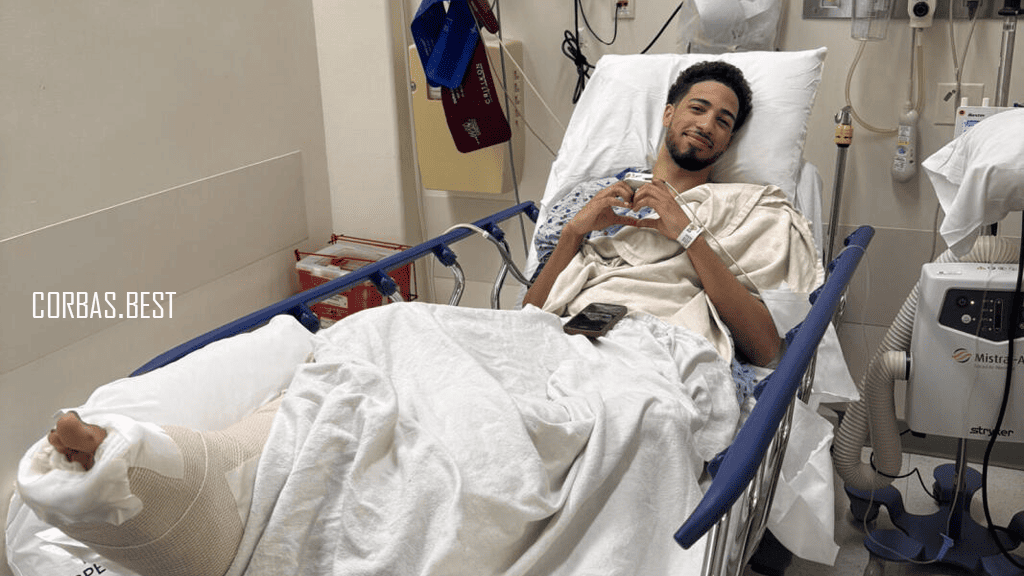
Curahan Hati Tyrese Haliburton Setelah Menjalani Operasi Achilles
Pendahuluan Curahan Hati Tyrese Haliburton Setelah Menjalani Operasi Achilles. Pada bulan tertentu, dunia basket dikejutkan…
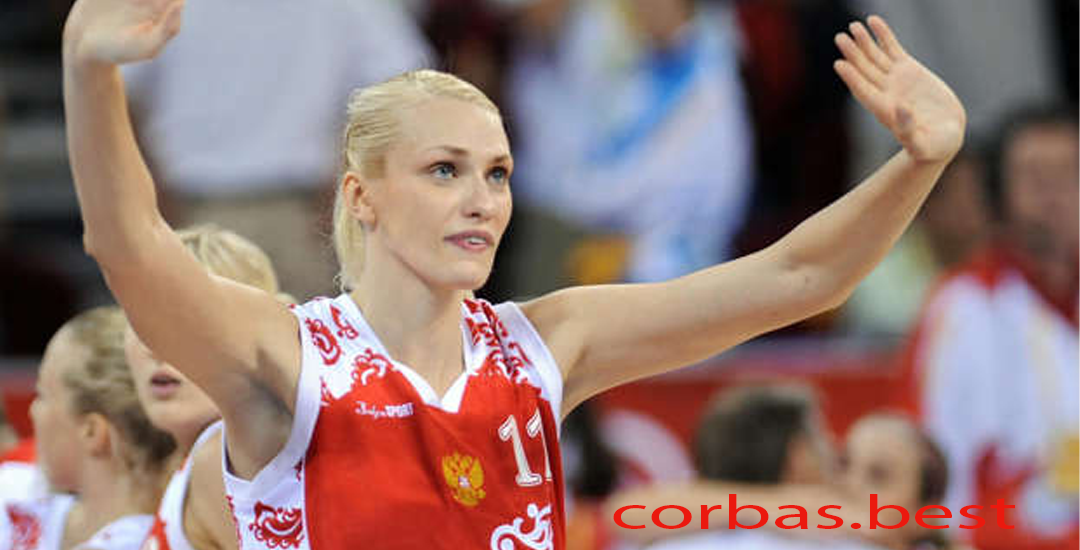
Maria Alexandrovna Stepanova: Bintang Basket Profesional dan Olimpiade Rusia
Pendahuluan Maria Alexandrovna Stepanova adalah salah satu pemain basket profesional paling terkenal dari Rusia, yang…
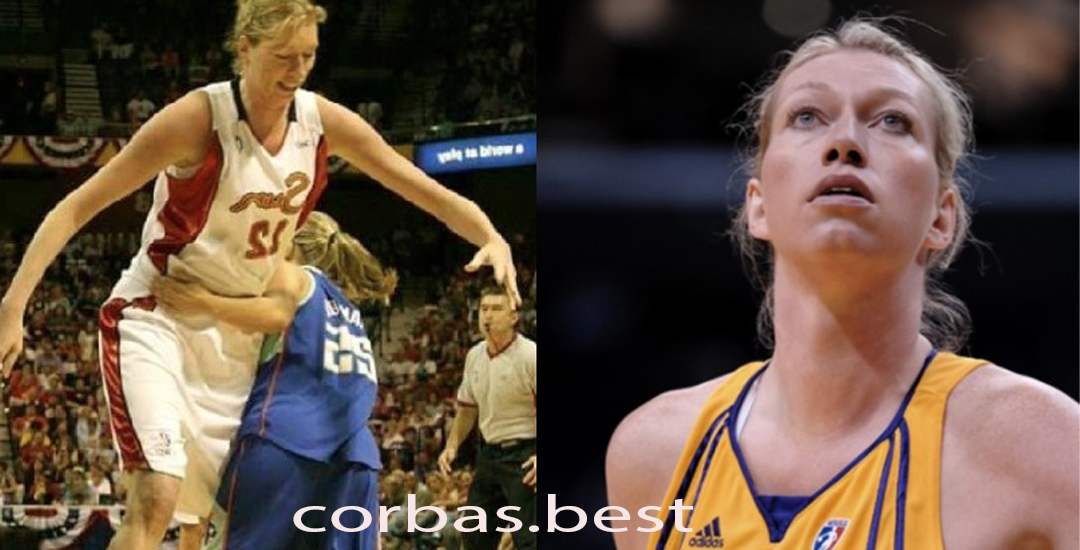
Małgorzata Dydek: Legenda Basket Wanita dari Polandia dan Amerika Serikat
Pendahuluan Małgorzata Dydek, yang lebih dikenal dengan panggilan Margo Dydek, adalah salah satu pemain basket…
Earvin Johnson Jr.: Legenda yang Dianggap Sebagai Pemain Point Guard Terbaik Sepanjang Masa
Pendahuluan Earvin Johnson Jr Dalam dunia basket profesional, beberapa nama telah melekat sebagai legenda yang…
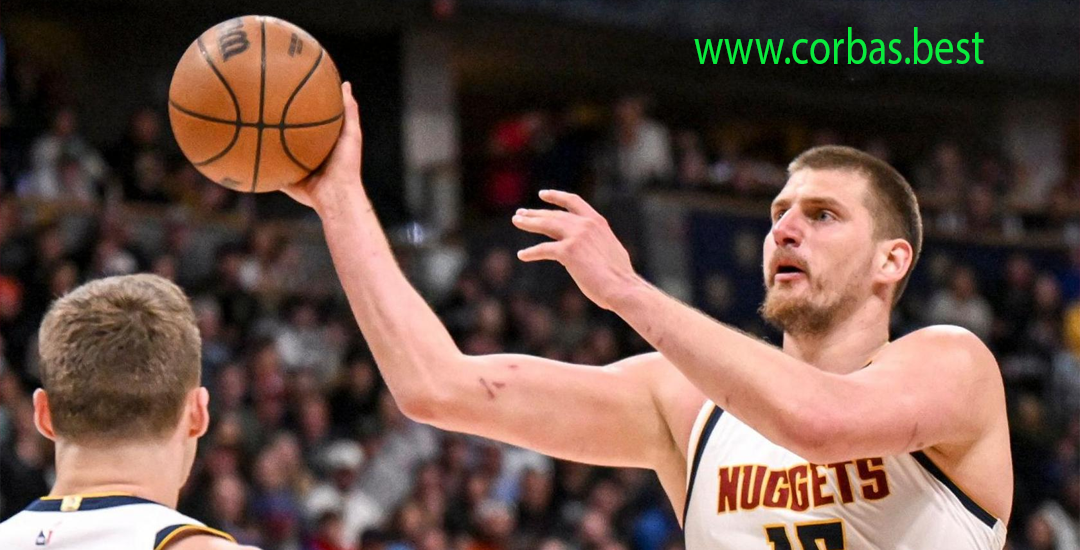
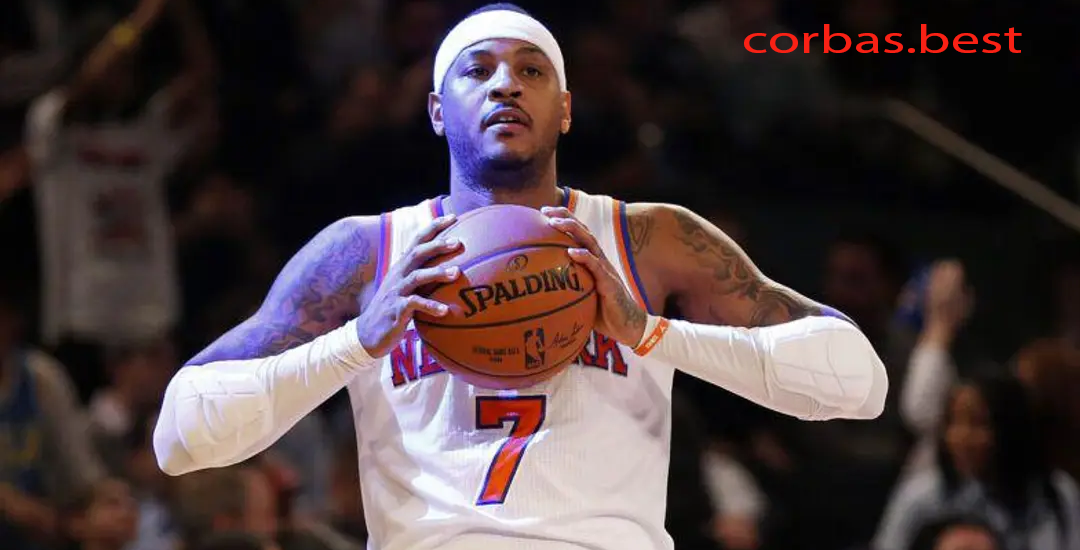
Carmelo Anthony Dipilih oleh Denver Nuggets di Tempat Ketiga pada Draft NBA 2003
Pendahukluan Carmelo Anthony, salah satu pemain paling berpengaruh dan berbakat dalam sejarah NBA, memulai perjalanan…
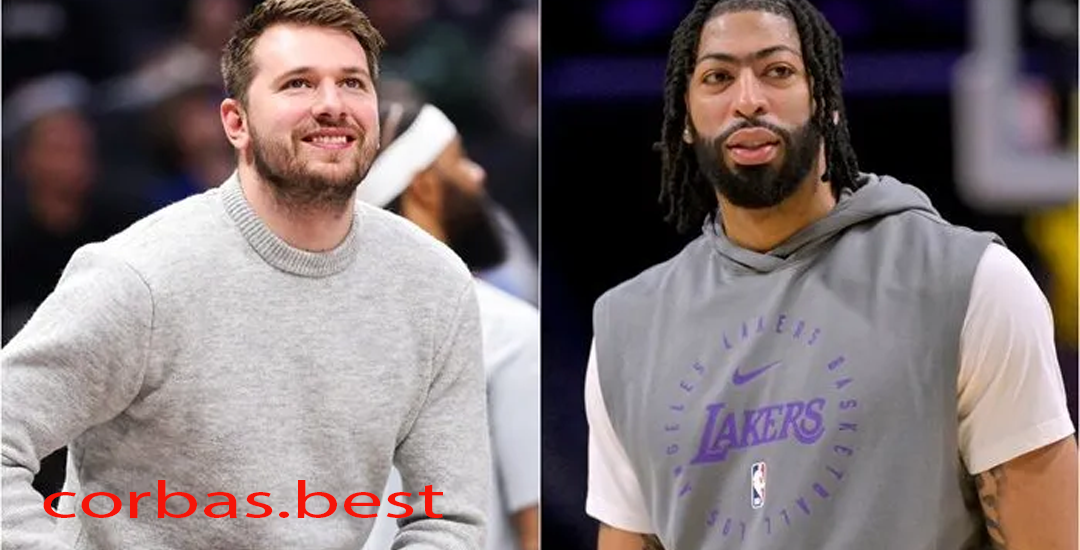
Dallas Mavericks dan Los Angeles Lakers: Meningkatkan Kompetisi dengan Luka Doncic dan Anthony Davis
Pendahuluan Dallas Mavericks dan Los Angeles Lakers Dalam dunia bola basket NBA, perdagangan pemain selalu…