RJ Barrett: Pemain Serba Bisa yang Dipilih New York Knicks dan Pernah Satu Tim dengan Zion
Pendahuluan RJ Barrett merupakan salah satu bintang muda potensial di dunia bola basket NBA. Pemain…
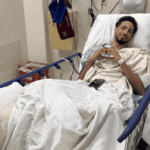
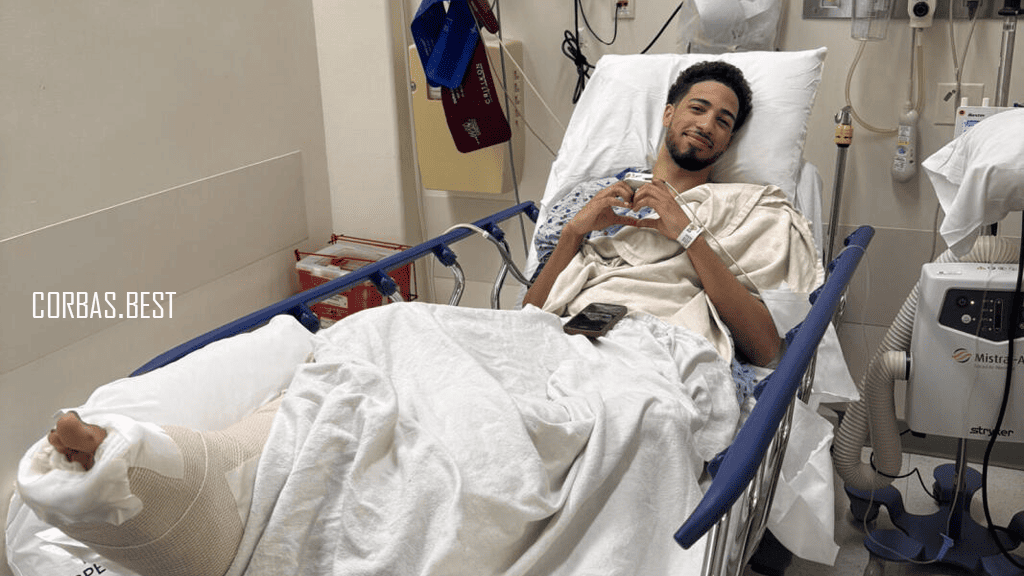
Curahan Hati Tyrese Haliburton Setelah Menjalani Operasi Achilles
Pendahuluan Curahan Hati Tyrese Haliburton Setelah Menjalani Operasi Achilles. Pada bulan tertentu, dunia basket dikejutkan…
Maria Alexandrovna Stepanova: Bintang Basket Profesional dan Olimpiade Rusia
Pendahuluan Maria Alexandrovna Stepanova adalah salah satu pemain basket profesional paling terkenal dari Rusia, yang…
Małgorzata Dydek: Legenda Basket Wanita dari Polandia dan Amerika Serikat
Pendahuluan Małgorzata Dydek, yang lebih dikenal dengan panggilan Margo Dydek, adalah salah satu pemain basket…
Earvin Johnson Jr.: Legenda yang Dianggap Sebagai Pemain Point Guard Terbaik Sepanjang Masa
Pendahuluan Earvin Johnson Jr Dalam dunia basket profesional, beberapa nama telah melekat sebagai legenda yang…
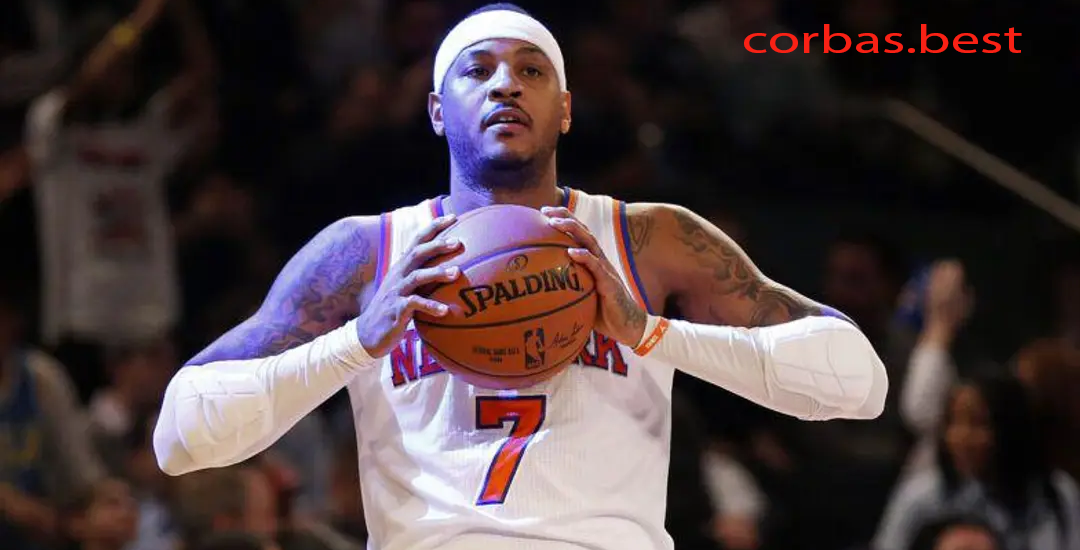
Carmelo Anthony Dipilih oleh Denver Nuggets di Tempat Ketiga pada Draft NBA 2003
Pendahukluan Carmelo Anthony, salah satu pemain paling berpengaruh dan berbakat dalam sejarah NBA, memulai perjalanan…
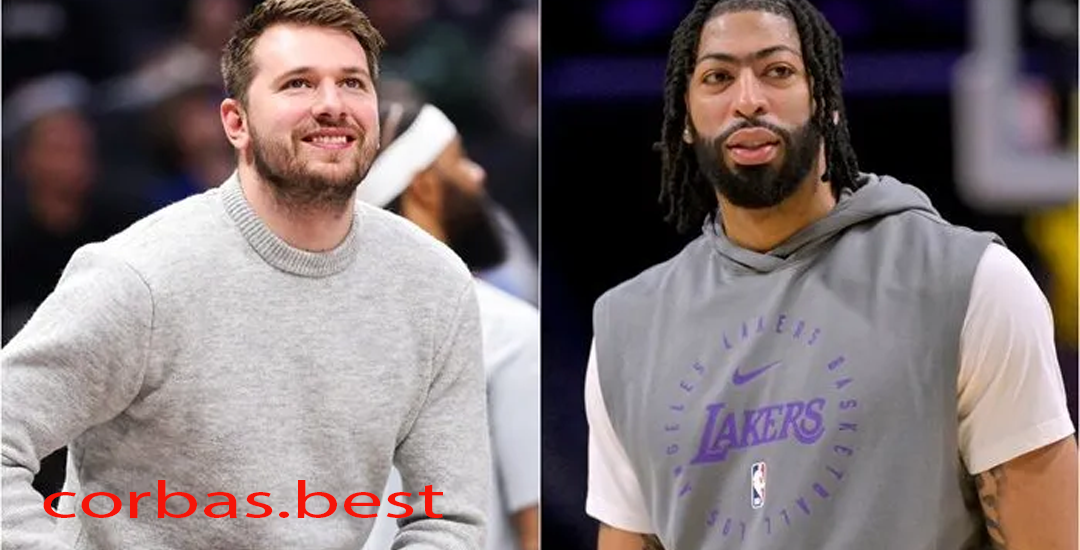
Dallas Mavericks dan Los Angeles Lakers: Meningkatkan Kompetisi dengan Luka Doncic dan Anthony Davis
Pendahuluan Dallas Mavericks dan Los Angeles Lakers Dalam dunia bola basket NBA, perdagangan pemain selalu…
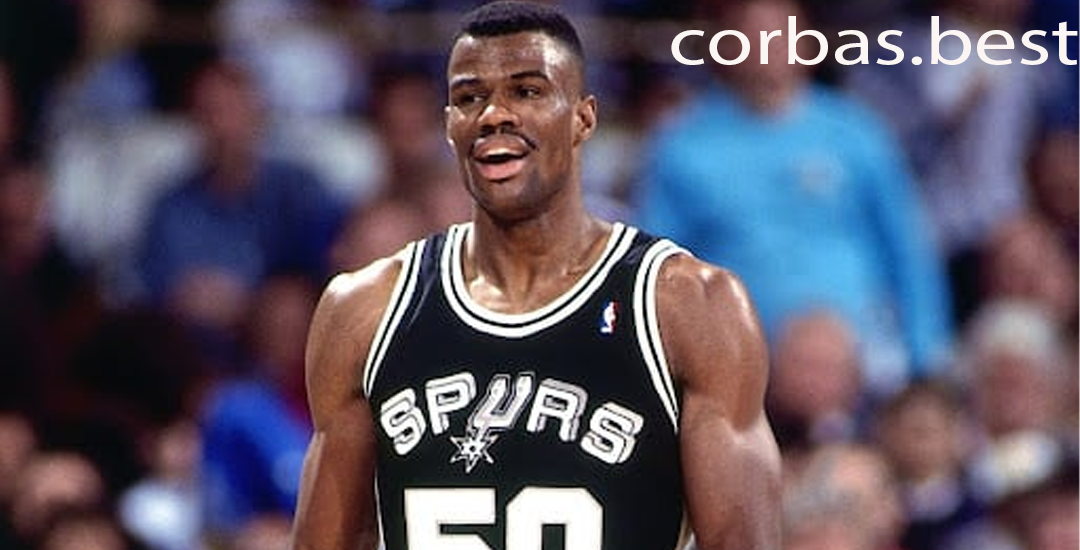
David Robinson: Legenda yang Mendalam di Hati Para Penggemar San Antonio Spurs
Pendahuluan David Robinson, yang dikenal dengan julukan "The Admiral," adalah salah satu pemain basket paling…
Theo Ratliff: Pemain Serba Bisa yang Dipilih oleh Detroit Pistons di Urutan ke-18 NBA Draft
Pendahuluan Theo Ratliff merupakan salah satu pemain yang dikenal karena keunggulan defensif dan kemampuannya bermain…
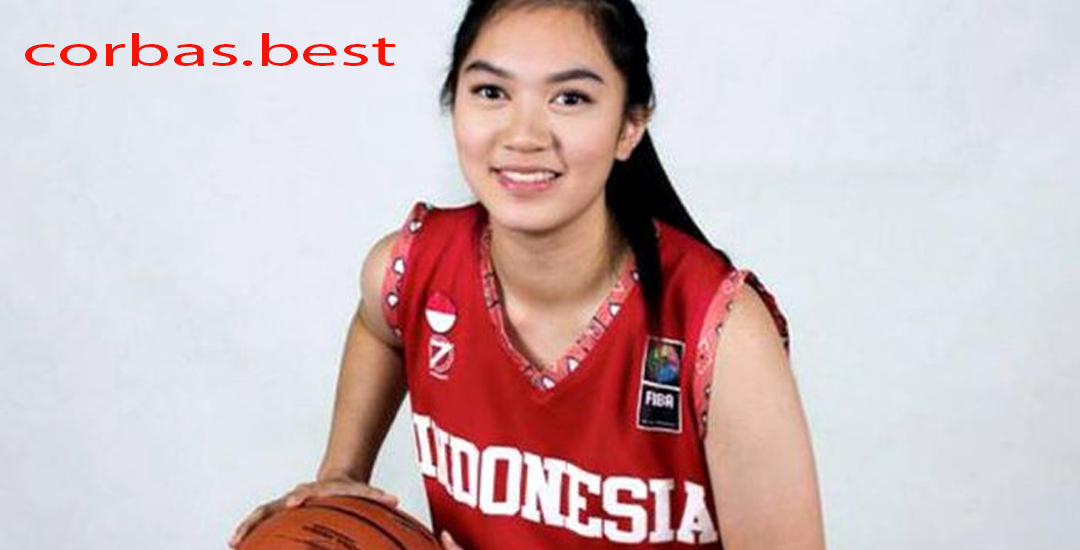
Grace Jesslyn Rasali: Pebasket Muda Berbakat dan Inspiratif dari Indonesia
Pendahuluan Grace Jesslyn Rasali Dalam dunia olahraga bola basket nasional, munculnya pemain muda berbakat dan…